Lista Encadeada (Linked List)
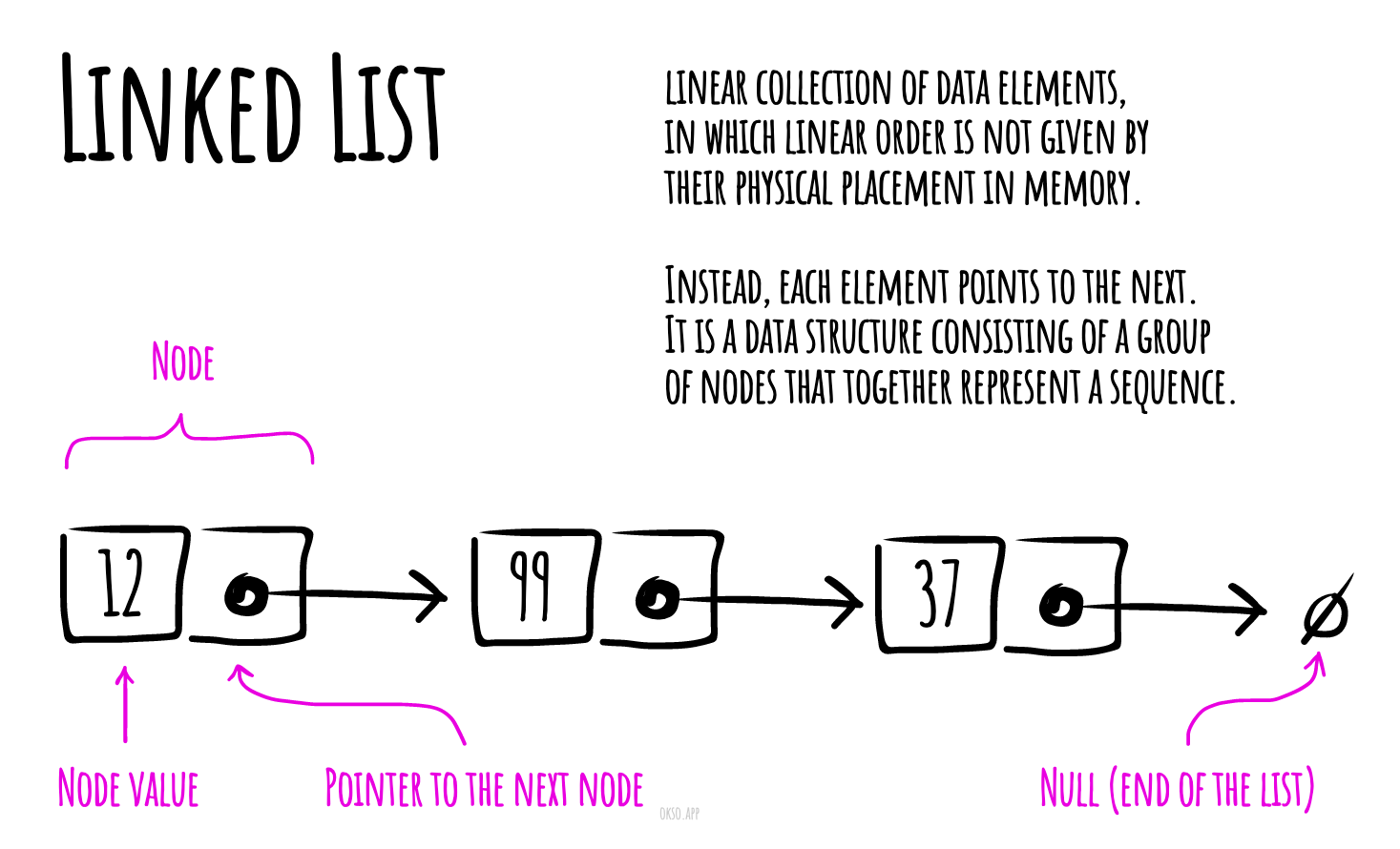
Na ciência da computação, uma lista encadeada é uma coleção linear de elementos de dados, em que a ordem linear não é dada por sua locação física na memória. Em vez disso, cada elemento aponta para o próximo. É uma estrutura de dados consistindo em um grupo de nós que juntos representam uma sequência. Sob a forma mais simples, cada nó é composto de dados e uma referência (em outras palavras, uma ligação/conexão) para o próximo nó na sequência. Esta estrutura permite inserção ou remoção eficiente de elementos de qualquer posição na sequência durante a iteração.
Variantes mais complexas adicionam ligações adicionais, permitindo uma inserção ou remoção mais eficiente a partir de referências de elementos arbitrárias. Uma desvantagem das listas encadeadas é que o tempo de acesso é linear (e difícil de inserir em uma pipeline). Acesso mais rápido, como acesso aleatório, não é viável. Arrays possuem uma melhor localização de cache em comparação com listas encadeadas (linked lists).
Made with okso.app
Pseudo código para Operações Básicas
Inserção
Add(value)
Pre: value is the value to add to the list
Post: value has been placed at the tail of the list
n ← node(value)
if head = ø
head ← n
tail ← n
else
tail.next ← n
tail ← n
end if
end Add
Prepend(value)
Pre: value is the value to add to the list
Post: value has been placed at the head of the list
n ← node(value)
n.next ← head
head ← n
if tail = ø
tail ← n
end
end Prepend
Pesquisa
Contains(head, value)
Pre: head is the head node in the list
value is the value to search for
Post: the item is either in the linked list, true; otherwise false
n ← head
while n != ø and n.value != value
n ← n.next
end while
if n = ø
return false
end if
return true
end Contains
Remoção
Remove(head, value)
Pre: head is the head node in the list
value is the value to remove from the list
Post: value is removed from the list, true, otherwise false
if head = ø
return false
end if
n ← head
if n.value = value
if head = tail
head ← ø
tail ← ø
else
head ← head.next
end if
return true
end if
while n.next != ø and n.next.value != value
n ← n.next
end while
if n.next != ø
if n.next = tail
tail ← n
end if
n.next ← n.next.next
return true
end if
return false
end Remove
Travessia
Traverse(head)
Pre: head is the head node in the list
Post: the items in the list have been traversed
n ← head
while n != ø
yield n.value
n ← n.next
end while
end Traverse
Travessia Reversa
ReverseTraversal(head, tail)
Pre: head and tail belong to the same list
Post: the items in the list have been traversed in reverse order
if tail != ø
curr ← tail
while curr != head
prev ← head
while prev.next != curr
prev ← prev.next
end while
yield curr.value
curr ← prev
end while
yield curr.value
end if
end ReverseTraversal
Complexidades
Complexidade de Tempo
| Acesso | Pesquisa | Inserção | Remoção |
|---|---|---|---|
| O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(n) |
Complexidade de Espaçø
O(n)